Customers utilize Azure AD's Application Proxy for more and more scenarios and applications. So we've made App Proxy even more flexible by enabling more topologies.
You can create Application Proxy connector groups so that you can assign specific connectors to serve specific applications.
This capability gives you more control and ways to optimize your Application Proxy deployment.
Each Application Proxy connector is assigned to a connector group. All the connectors that belong to the same connector group act as a separate unit for high-availability and load balancing.
All connectors belong to a connector group. If you don't create groups, then all your connectors are in a default group. Your admin can create new groups and assign connectors to them in the Azure portal.
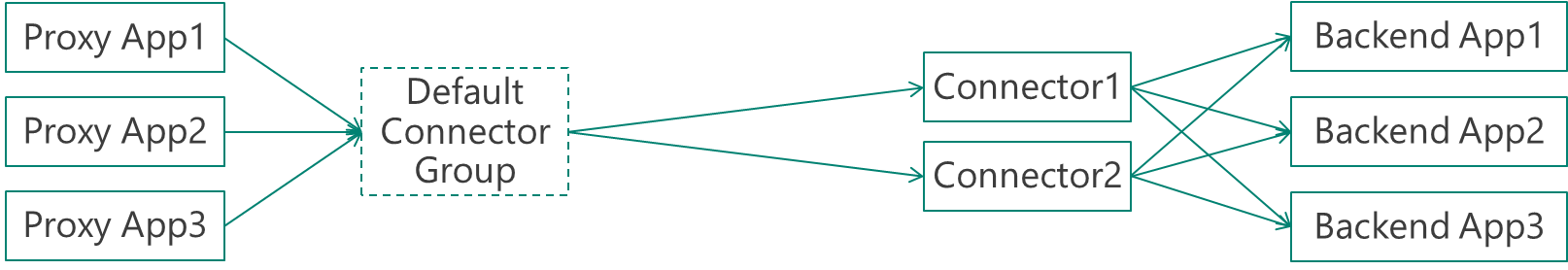
Default configuration – no use for connector groups
If you don’t use connector groups, your configuration would look like this:
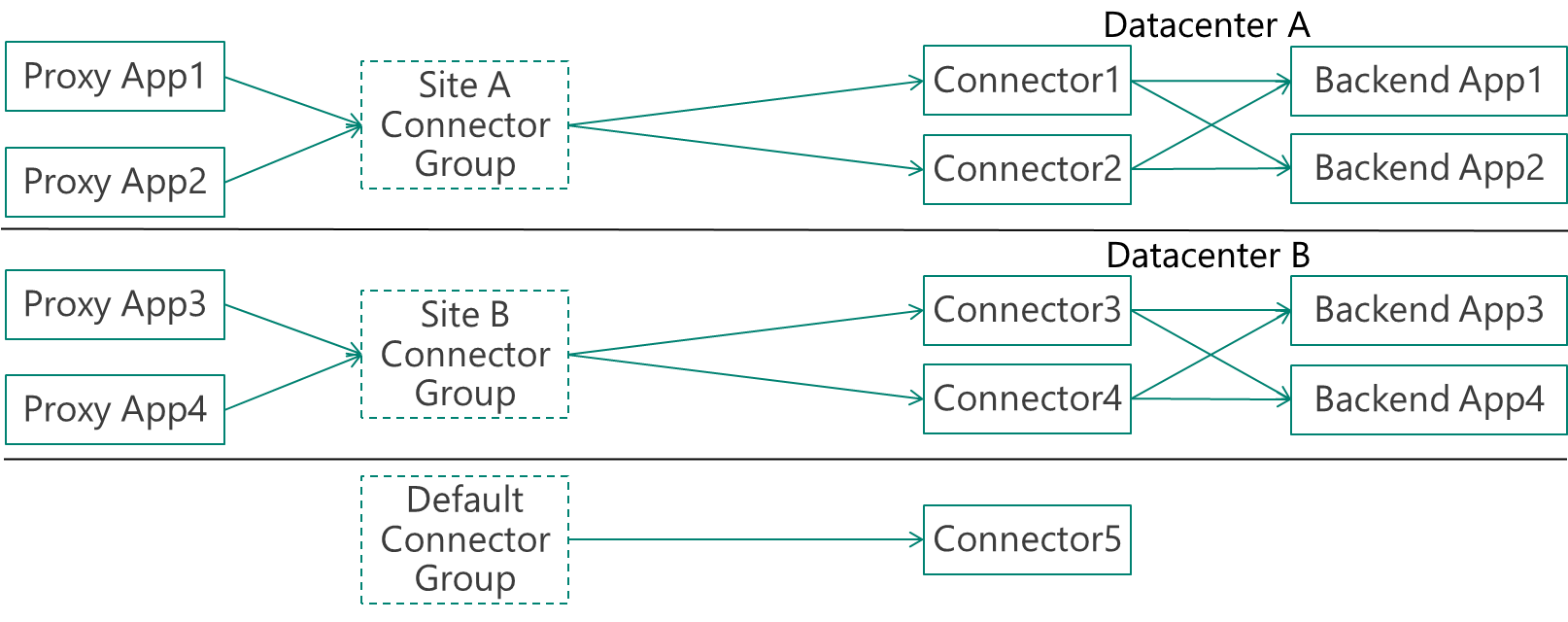
Recommended configuration – several specific groups and a default group for idle
The recommended configuration for large and complex organizations is to have the default connector group as a group that doesn’t serve any applications and is used for idle or newly installed connectors. All applications are served using customized connector groups. This enables all the complexity of the scenarios described above.
In the example below, the company has two datacenters, A and B, with two connectors that serve each site. Each site has different applications that run on it.
Comments