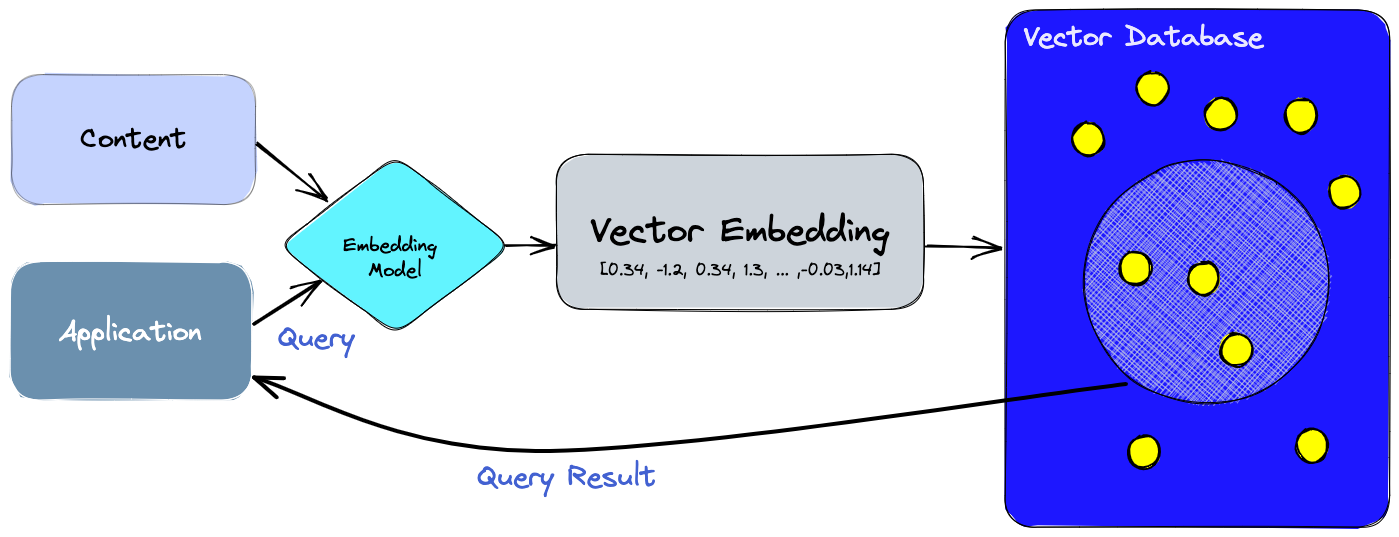
With a vector database, we can add advanced features to our AIs, like semantic information retrieval, long-term memory, and more. The diagram below gives us a better understanding of the role of vector databases in this type of application:
Embeddings are generated by AI models (such as Large Language Models) and have many attributes or features, making their representation challenging to manage. In the context of AI and machine learning, these features represent different dimensions of the data that are essential for understanding patterns, relationships, and underlying structures.
Steps:
- First, we use the embedding model to create vector embeddings for the content we want to index.
- The vector embedding is inserted into the vector database, with some reference to the original content the embedding was created from.
- When the application issues a query, we use the same embedding model to create embeddings for the query and use those embeddings to query the database for similar vector embeddings. As mentioned before, those similar embeddings are associated with the original content that was used to create them.
Comments